At approximately 12:35 hours on 12 May 2014, an unmanned train ran away for a distance of around 1.8 miles before colliding with a set of unattended coaches.
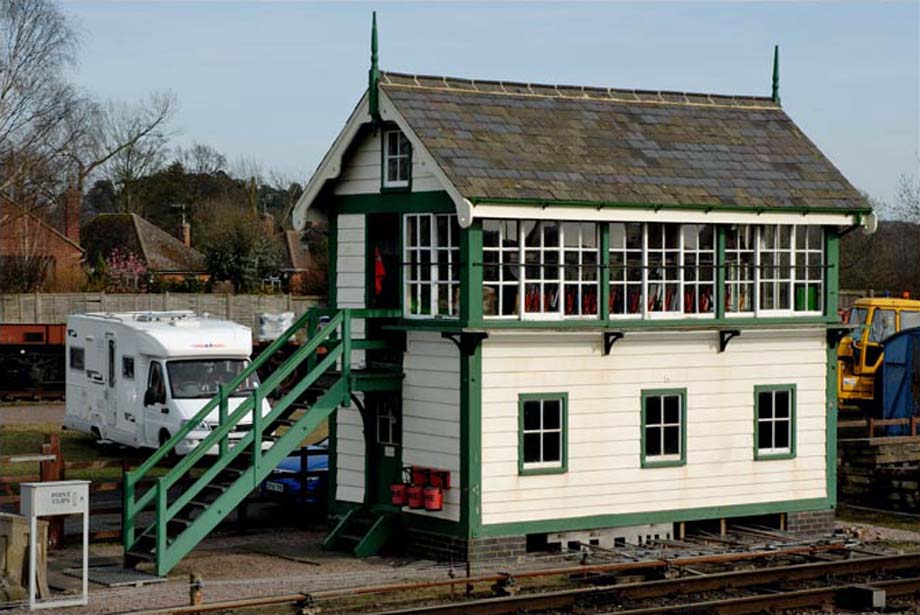
The collision occurred about 450 metres south of Loughborough Central station, located on the Great Central Railway (GCR).
This is a heritage railway, and no train services for public use were being operated on the day of the accident.
Nobody was injured as a result of the collision, although significant damage was sustained by some of the rail vehicles involved.
The train which ran away had been previously left unattended within a possession on a main line opposite Quorn signal box.
The railway at Quorn is on a gradient which descends towards Loughborough.
The train which ran away consisted of a locomotive coupled to a single coach.
RAIB's investigation found that, before the train was left unattended, the air brakes on the locomotive had been applied by the driver and a single wheel scotch had been positioned against one of the locomotive's wheels by a member of staff.
The handbrakes on the locomotive were not applied and the coach was not secured with either brakes or a wheel scotch.
RAIB has concluded that the train ran away because the wheel scotch was positioned against the locomotive's wheel in a way which made it ineffective.
The RAIB determined that the handbrakes on the locomotive, had they been used, would have provided sufficient braking force to have held the train.
The driver did not apply the locomotive's handbrakes because he believed that they were not effective on this class of locomotive and that the wheel scotch would provide sufficient braking force, should the pressure in the air braking system leak away.
The driver may also have been influenced by the prevailing practices on the railway which related to the use of handbrakes.
The train was not left in a location where it would have been protected from running away by the arrangement of the infrastructure.
This was probably because the staff involved thought that these locations were either not available or needed disproportionate time to access.
It may also have been because they had a reduced perception of the risks of leaving trains unattended outside of these locations.
RAIB found that checks by the Great Central Railway's managers did not detect the full-extent of the unsafe and non-compliant practices present within possessions.
The investigation also found that some of the rules relating to the way in which rail vehicles were to be left unattended were inconsistent and potentially unclear.
As a consequence of this investigation, RAIB has identified two key learning points.
These are, that the movement of trains not connected by a continuous automatic brake, or which do not include a brake van under the control of a guard should be avoided, and that safety critical activities must be undertaken by an adequate number of staff holding the correct competencies.
RAIB has also made four recommendations addressed to the Great Central Railway.
These relate to, ensuring that activities which result in trains being left unattended are subject to effective risk controls, implementing the railway's safety management system to ensure that its requirements relating to the training and assessment of staff are effective, ensuring that non-compliances and unsafe practices are detected in the future, and ensuring that the Great Central Railway has effective oversight of the maintenance being undertaken on diesel locomotives operating on its infrastructure.
Author unknown.
(likely no image with original article)
(usually because it's been seen before)
provisions in Section 29 of the
Canadian Copyright Modernization Act.